 People are accustomed to treating the washing machine as an ordinary, routine part of the interior. But a couple of centuries ago, no one could even imagine such technically complex devices. Today they are found in almost every home, helping housewives with washing and drying clothes. Pledge safe, efficient operation – carefully study the attached instructions. And knowledge of the internal structure of equipment can directly help with repairs. The electrical circuit of a washing machine is not as complicated as it seems at first glance. Our article will help you with this.
People are accustomed to treating the washing machine as an ordinary, routine part of the interior. But a couple of centuries ago, no one could even imagine such technically complex devices. Today they are found in almost every home, helping housewives with washing and drying clothes. Pledge safe, efficient operation – carefully study the attached instructions. And knowledge of the internal structure of equipment can directly help with repairs. The electrical circuit of a washing machine is not as complicated as it seems at first glance. Our article will help you with this.
All modern washing machines have approximately the same set of functions and modes. There may be minor differences in the methods of loading laundry and additional spin programs. The general electrical diagram of the washing machine will help you understand the principle of operation of this equipment, this will have a positive effect on the service life, capabilities fix a minor problem yourself.
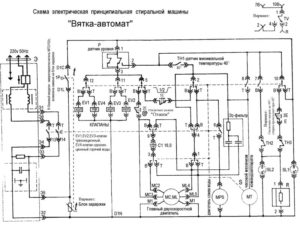
General scheme. Basic parts of the washing machine
Not every user can understand the electrical circuit of a washing machine, but it won’t hurt to learn about the basic systems. The pictures below show the following components, which are found in almost every washing machine:
- counterweight;
- water level relay (sensor);
- noise suppression filter;
- drain filter;
- pump (pump);
- drain hose;
- drum motor;
- tubular electric heater (TEH);
- start-up voltage relay;
- power block;
- thermostat;
- inlet hose;
- drum pulley;
- drum (tank);
- dispenser;
- detergent supply system;
- drum springs;
- solenoid valve.
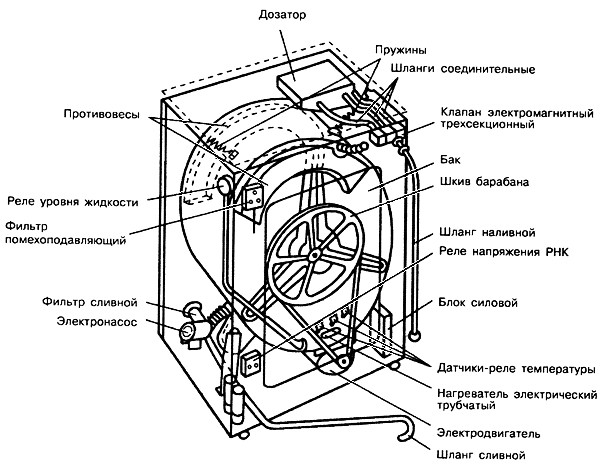
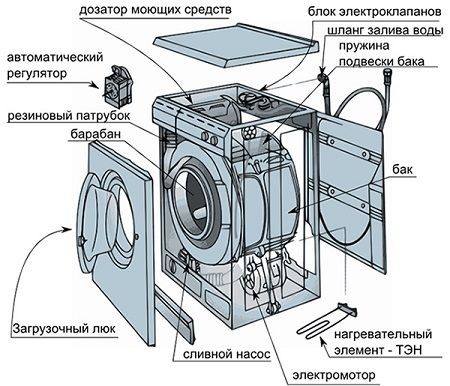
Control system
All modern automatic washing machines equipped with some kind of computer that processes information from sensors, controls the supply and drainage of water, and switches cleaning programs. The number of programs that are installed in the control module varies depending on the model. The presence or absence of particularly convenient washing modes has a significant impact on the price of the unit.
The cause of the breakdown can be either a failure in the operating system or failure of electrical components and sensors. Broken electronics usually cannot be repaired. Here is a list of those relays whose failure will not allow you to start washing.
- Water level sensor (pressostat). Reports the amount of water in the drum.
- Thermostat. Built into the drum from the bottom, it regulates the temperature of the liquid.
- Drum rotation speed sensor.
Solenoid valve
This module is responsible for filling the drum with water. Works in conjunction with a pressure switch. When the valve receives a signal that there is enough liquid in the tank, it closes and water stops flowing.
Drum motor
Represents a standard electric motor. Rotates the drum, transferring the energy of movement through a belt drive to a pulley.The speed and direction of rotation are set by the control system taking into account the indicators of the speed sensor.
Loading hatch
The door located on the front panel. Before starting the wash, the control system locks it so that the user cannot accidentally open the hatch while there is water in the tank. The latest Ariston models have the function of loading items during washing through a special compartment. Through it, the clothes are loaded into the drum.
A heating element
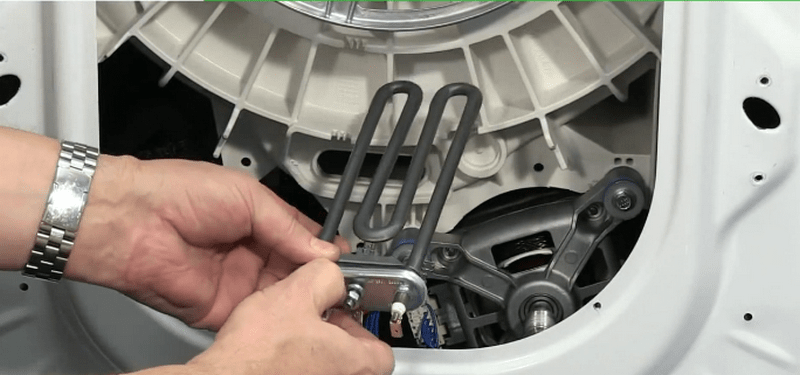
Begins to heat the water in the tank upon command from the control system. At this time, the thermostat begins to measure the temperature. When it reaches the required value, the heating element turns off. The most common cause of failure of this part is the formation of a thick layer of salt deposits (scale) on it. This layer impairs heat transfer, which leads to systematic overheating of the metal tube.
Use cleaning products along with powder to prevent deposits from forming on the heating element. Samsung supplies its washing machines with heating elements that are extremely resistant to scale formation. This is achieved through a double ceramic coating.
Drain pump
Before starting the spin program, all water is drained from the tank. A pump is involved in this process. It consists of filter and electric motor with impeller. The cause of pump failure may be failure of the electric motor or general contamination of the system.The filter is located at the bottom of the front of the housing in most washing machines.
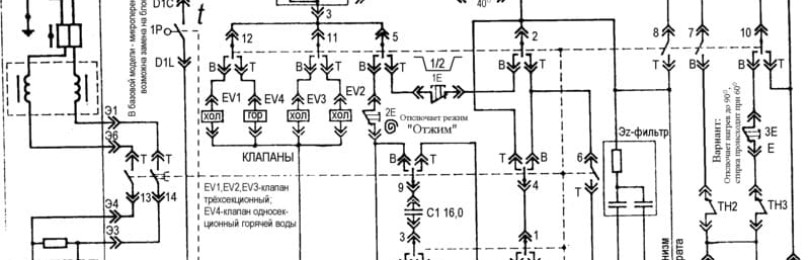
Examples of electrical circuits of washing machines
A circuit diagram can help you diagnose faults using a network tester. Understanding them on your own is an extremely difficult task. Without appropriate energy education and experience in handling microelectronic circuits, it will be extremely difficult to read these drawings.
To better understand what is depicted in these diagrams, some of the most commonly used symbols will be explained below them.
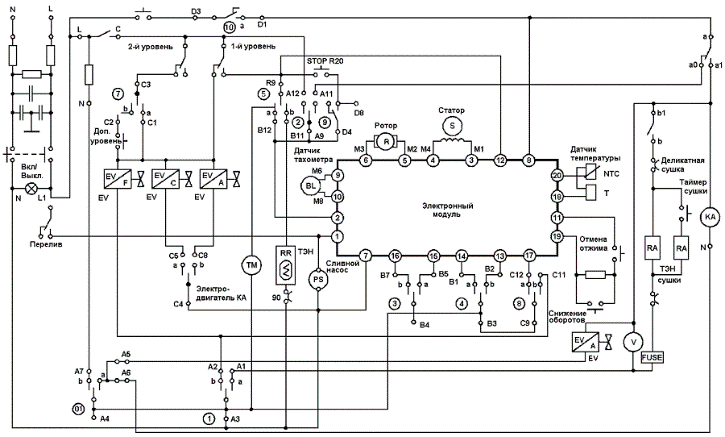
Ariston washing machine diagram
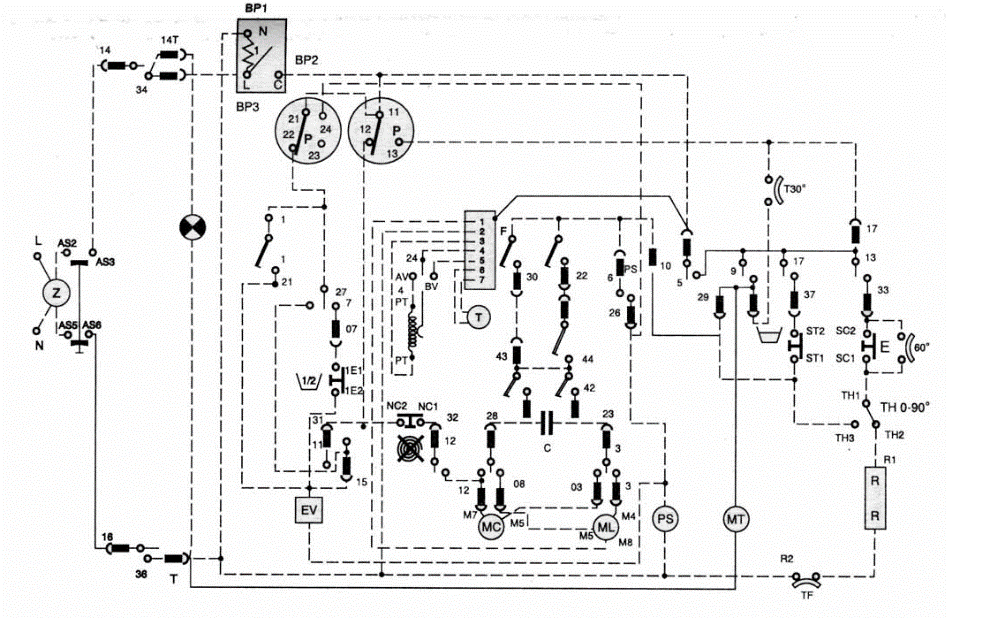
Ardo washing machine diagram
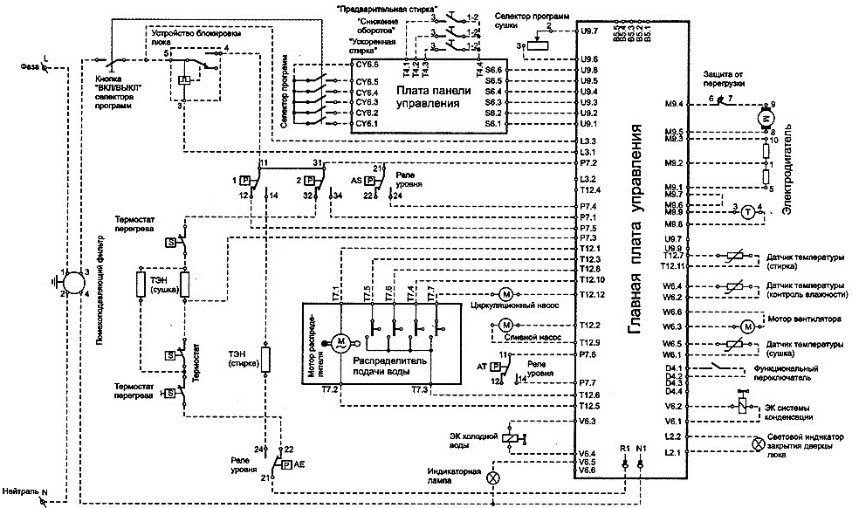
Electrolux washing machine diagram
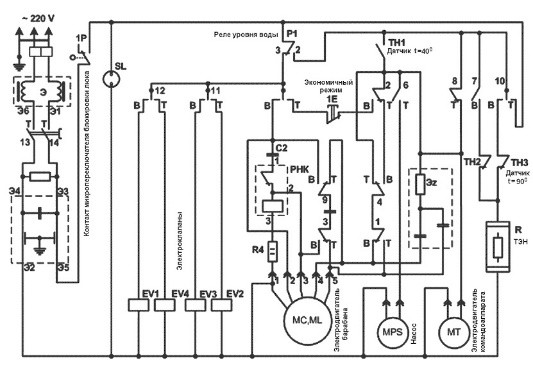
Kandy Scheme
- AQS – solenoid valve;
- B – buzzer (device for supplying audio signals);
- BP – hatch door locking mechanism;
- ET – thermostat (off);
- EV – solenoid valve;
- I – inverter (switch);
- IP – fuse;
- L – line;
- M – main electric motor/grounding;
- MC – electric motor/spin winding;
- MI – asynchronous electric motor
- ML – electric motor/wash winding
- MO – box;
- MP – hatch door switch;
- MR – magnetic lock;
- N – neutral/block;
- NTC – temperature sensor;
- P – pressure sensor;
- PM – relay protection of the electric motor;
- PS – drain pump;
- R – heating element resistor;
- RR, RTF – heating element;
- T – drum rotation speed sensor;
- TH – temperature sensor.
Electrical connection
Washing machines are placed in bathrooms, kitchens, and hallways.During installation, pay attention to the outlet into which you are going to connect the equipment. Remember, the heating element places an extremely large load on your home's energy system. Therefore, connect the washing machine only to outlets that are grounded.
Gathered install a washing machine in the kitchen Do not under any circumstances connect it to double sockets together with other powerful equipment. This can lead to power surges and broken plugs. If the washing machine is in the bathroom, make sure that the outlet is not exposed to moisture. Poor wiring and power surges in the network are a common cause of failure of the most sensitive components (sensors, microelectronics). Treat the connection of equipment as responsibly as the choice.








Congratulations, great idea and timely